Abstract
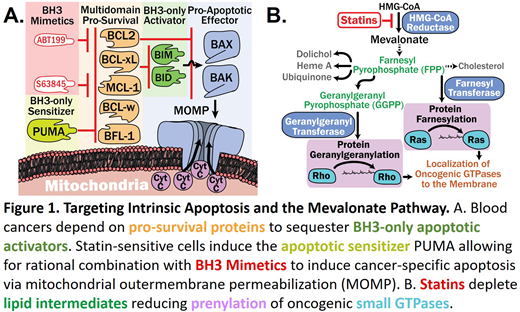
Multiple Myeloma (MM) is a disease of malignant plasma cells for which if left untreated, patients face a 6 month median survival (Osgood, 1960). New agents and combinations continue to improve MM outcomes, extending the median survival to 5 years; however, patients will ultimately succumb to the disease after exhausting treatment options (Fonseca et al., 2017). A novel class of drugs, BH3 mimetics, specifically inhibit the gatekeepers of apoptosis known as pro-survival BCL2 family members BCL2, MCL1 and BCL-xL (Figure 1A). BCL-2 selective BH3 mimetic, venetoclax (ABT-199), has shown promise in a subset of MM patients; however, combinations are required to improve the depth of response. (Moreau et al., 2017)
Our lab is pioneering the novel combination of apoptosis-promoting BH3 mimetics with the cancer-killing effect of statins in blood cancers (Lee et al., 2018). Statins are FDA-approved for their ability to lower cholesterol by blocking the synthesis of a key precursor: mevalonate, a major biosynthetic substrate (Figure 1B). Inhibition of the mevalonate pathway by statins stops the synthesis of intermediates necessary for small GTPase function, providing an attractive avenue for targeting these "undruggable" oncogenes (Berndt, Hamilton, & Sebti, 2011; ten Klooster & Hordijk, 2007). Though this potential has been long recognized, previous work on repurposing statins reported effective concentrations that are well above the plasma levels typically achieved in patients receiving standard doses for hypercholesterolemia (Ahmed, Hayslip, & Leggas, 2013; Björkhem-Bergman, Lindh, & Bergman, 2011; van der Spek et al., 2006). Furthermore, previous studies provided insufficient rationale for mechanism-based combination strategies. We have achieved a breakthrough towards this goal by combining statins with the BCL2-specific BH3 mimetic, venetoclax. Our retrospective analysis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) clinical trial data revealed that subjects taking statins at the FDA-approved dose had significantly higher frequency of complete remissions following venetoclax treatment (Lee et al., 2018). Through mechanistic studies we showed that statins increase expression of the pro-apoptotic, BH3-only sensitizer PUMA, thereby synergizing with venetoclax to induce apoptosis in various leukemia and lymphoma cell types.
Our current work leverages these findings to treat MM. Retrospective analysis of clinical trials of venetoclax in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone in the venetoclax-sensitive subset of MM demonstrates a similar trend as in the CLL clinical trials in support of background doses of statins (Roberts et al., 2017). Pre-clinical results of MCL-1 BH3 mimetics in development support their future use in MM (Kotschy et al., 2016). Based on these data, we tested two BH3 mimetics, venetoclax and a pre-clinical MCL-1 inhibitor, S63845. Using a panel of 9 human MM cell lines, the data demonstrate that statins potentiate BH3 mimetic-induced apoptosis as measured by reductions in BH3 mimetic IC50. Sensitivity to the combination was maintained in both MM1R and MM1S, MM lines from the same origin that model glucocorticoid resistance and sensitivity respectively, while venetoclax combination with dexamethasone was lost in MM1R cells (Greenstein et al., 2003; Matulis et al., 2016). Additionally, combination-sensitive cell lines corroborate a p53-independent induction of PUMA expression. These data suggest that BH3 mimetic and statin combination may be useful in the clinical settings of dexamethasone resistance and high risk p53-null (17p deleted) patients. To further guide the appropriate application of BH3 mimetics and statins, we are validating that dynamic BH3 profiling can predict efficacy of statins in combination-sensitive versus non-sensitive MM lines. Moreover, preliminary ex vivo studies on freshly isolated CD138+ MM cells from patient bone-marrow aspirates demonstrate combined killing with BH3 mimetics and statins. Ongoing studies will investigate the dependence on upstream GTPase signaling on survival and PUMA upregulation.
Brem:Bayer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genetech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pharamcyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal